Your 3D Printing Journey: Slicer, CAD and more
3D printing technology has revolutionized the way we bring our ideas to life. From prototyping to manufacturing, this innovative process offers unparalleled possibilities. However, at the heart of every successful 3D print lies a well-designed 3D model and the software tools that facilitate its creation.
The software serves as the backbone of 3D printing, enabling users to transform their concepts into precise and intricate digital models. CAD software, in particular, plays a fundamental role in the design process, allowing users to create, modify, and optimize 3D models with ease. Additionally, slicers are essential software tools that convert digital models into instructions that 3D printers can understand, turning virtual designs into tangible objects.
Understanding the different software options available and their functionalities is crucial for avoiding headaches and achieving optimal results in 3D printing. Let us guide you through the most important pieces of software you will need to dive into the world of 3D printing and modeling.

CAD Software
CAD software, short for Computer-Aided Design software, is a cornerstone of the 3D designing process. It empowers users to create, modify, and refine intricate 3D models precisely and efficiently. CAD software provides a virtual workspace where designers can bring their ideas to life before the physical printing stage.
So what are the most popular CAD software options?
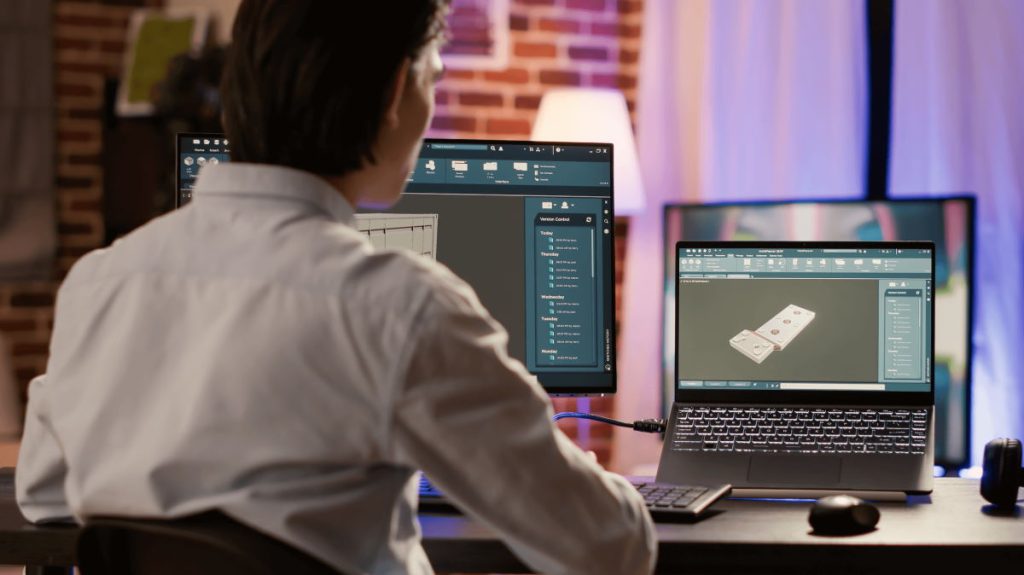
Autodesk Fusion 360
Autodesk Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD software widely utilized in the 3D printing and design community. It provides parametric modeling capabilities, allowing users to easily create complex designs. Moreover, its sculpting and organic shape-creation tools enable the realization of intricate and artistic designs. The interface is user-friendly, with a clean and polished look. One of the main selling points is its cloud functionality, which allows multiple people to work on the design in real-time.
This is a paid software but if you want it just for personal use, you can get a limited, free version. There is also available a free trial of the software with full functionalities. The cost is 535$ per year.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is another highly regarded CAD software widely used in the field of 3D printing and design. It has a bit steeper learning curve compared to Fusion 360. Solidworks brings a decent amount of 3D modeling tools, with the exception of sculpting. The interface feels a bit overwhelming with all the small buttons and icons. A key disadvantage compared to Fusion 360 is that SolidWorks only work on Windows computers. This means that if you want to run it on Mac, you will need to set up a virtual machine with Windows first.
SolidWorks is also a paid CAD software. Unfortunately, the prices are noticeably higher compared to Fusion 360. There are different packages available but all come with a license fee and an annual maintenance fee, Depending on the package, the license fee may cost between $4000 and $8000 and the annual maintenance fee is between $1300 and $2000. There is also a free trial available.
TinkerCAD
CAD software has a steep learning curve. Once you have some experience with the software, things will become way easier but at first, you might feel a bit lost. That’s why simple 3D modeling software such as TinkerCAD has become so popular. It features a user-friendly interface and a wide selection of pre-designed shapes and objects, allowing users to quickly create 3D models by combining and manipulating basic geometric shapes. Getting started is extremely easy even and that makes it an ideal choice for educators, students, and hobbyists. Of course, anyone serious about 3D modeling and design will find TinkerCAD quite limiting after a few hours of “tinkering” with it.
TinkerCAD is completely free. It’s also a web app, so you can use it on different computers easily.
By leveraging the capabilities of CAD software, users can unleash their creativity, iterate on designs, and ensure the feasibility of their models before proceeding to the printing phase. These software tools empower individuals and professionals alike to push the boundaries of what is possible with 3D printing technology.
Slicers
Once you have a well-designed 3D model, the next step in the 3D printing process is to prepare it for printing. This is where slicers come into play. Slicers are software tools that take the digital 3D model and transform it into a format that 3D printers can understand and execute. They slice the model into thin layers and generate a set of instructions, known as G-code, which instructs the printer on how to build the object layer by layer.
With the help of slicers, users can change the parameters of their 3D models. Probably the most important settings to change are the layer height, number of walls, infill density, and print speed. But of course, there are more advanced features for users that want to have full control of their prints - infill pattern, ironing, acceleration, print speed, wall and infill width, retraction, and many more.
It’s important to note that a setting that does the exact same thing can have different names on the other slicers.
But what are some of the most popular slicers?
- Cura
- PrusaSlicer
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
Slicers are constantly updated with new and improved features and it’s recommended to stay up-to-date with them. Though some more experienced users love the way that their current slicers perform and never update theirs. Whatever you choose, understand the pros and cons of each.
If you are just starting with 3D printing and you have found a guide for a certain slicer, don’t be afraid to try it. There is no industry standard and professionals and enthusiasts use whatever they find comfortable and have set proper settings for their printers. Although using the same settings as someone else who is using the same printer most likely won’t result in identical results, it will be a great starting point.
Advanced 3D printing software
In addition to CAD software and slicers, there are several other software tools that can greatly enhance your 3D printing and design workflow. Let's explore a few notable options:
For STL Repair - MeshMixer
This free software allows users to evolve their existing CAD designs into parts that are optimized for 3D printing. Some of the features it offers include:
- Mesh repair and optimization
- Mixing and mesh combination
- Sculpting
- Preparing models for multicolor printing
- Custom supports generation
Sometimes it’s not necessary to edit a 3D design in CAD software. There are tools like MeshMixer that provide all the features one might need to make small adjustments and optimize their stl files.
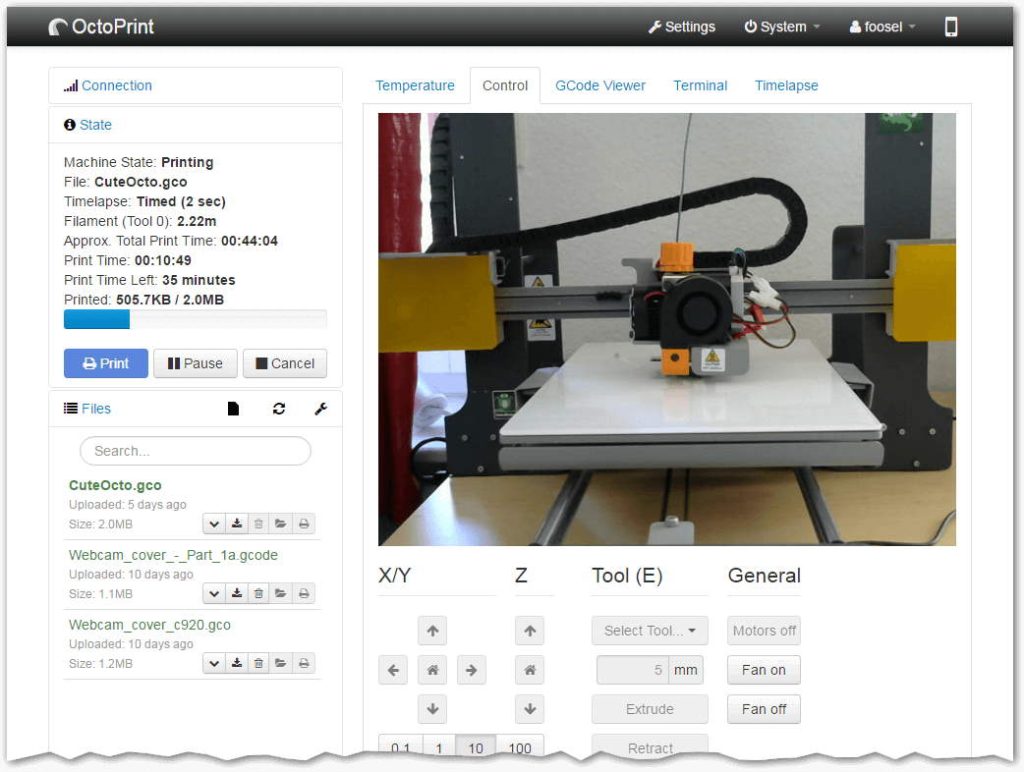
For Remote Print Control - OctoPrint
OctoPrint is a powerful software tool specifically designed for managing and controlling 3D printers remotely. It provides a user-friendly interface accessible through a web browser, allowing users to monitor and control their 3D printers from anywhere with an internet connection. OctoPrint has features such as:
- live video streaming
- print job monitoring
- the ability to start, pause, or cancel prints remotely
- plugin system that extends its functionality with additional features and integrations
With OctoPrint, users can conveniently manage their print jobs, monitor progress, and ensure smooth and reliable printing without being physically present at the printer. This software tool enhances the accessibility and convenience of 3D printing, making it a valuable addition to your workflow.
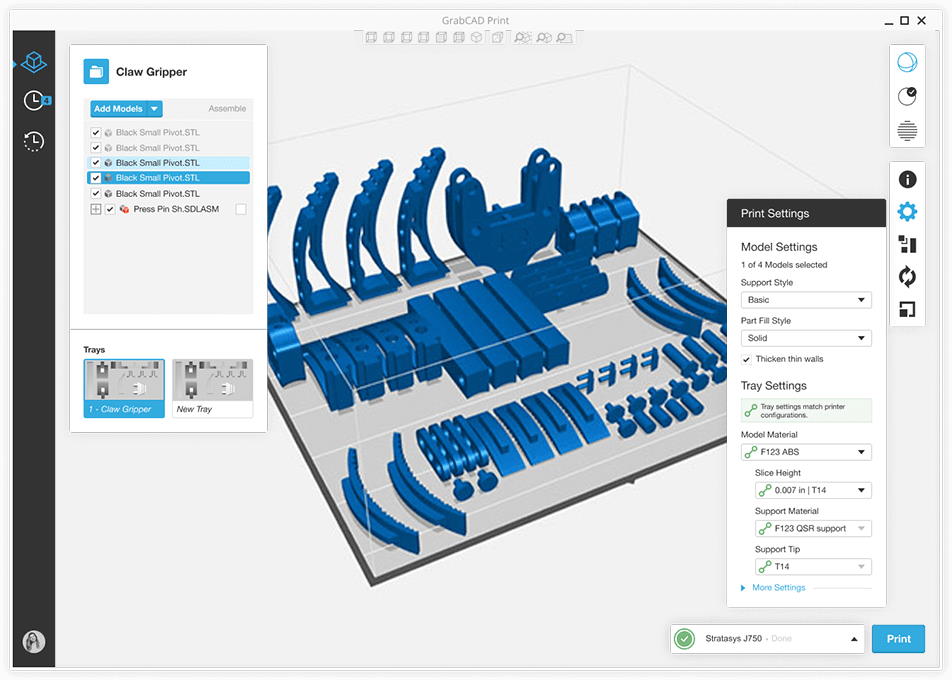
To Simplify Workflow - GrabCAD Print
GrabCAD Print is a software tool specifically designed to simplify the 3D printing process. It offers a streamlined workflow and optimized print settings, making it easier for users to achieve high-quality prints with minimal effort. GrabCAD Print supports a wide range of 3D printers and provides features such as automatic orientation, print previews, and remote monitoring. By automating many aspects of the printing process, GrabCAD Print helps users save time and achieve consistent, reliable results. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, GrabCAD Print can significantly enhance your 3D printing experience.
These additional software tools complement the functionality of CAD software and slicers. They provide essential capabilities for inspecting and preparing models, optimizing print settings, and simplifying the printing process.
Which software to use for 3D printing?
Utilizing the right software tools is essential for successful 3D printing and designing. CAD software empowers users to create and modify intricate 3D models, while slicers bridge the gap between virtual designs and physical prints. Other software is not necessarily needed to start printing but can greatly help with workflow optimization.
Continuously learning and experimenting with these software tools will help you unlock the full potential of 3D printing and design.
