3D Printing Techniques: Comparing SLA and FDM
3D printing technology has made it possible for businesses and individuals to create their own three-dimensional objects with ease. Two of the most popular techniques are SLA and FDM, each with its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. In this article, we'll take a closer look at both SLA and FDM printing, comparing the two to help you decide which technique is best for your specific needs.
What is SLA Printing?
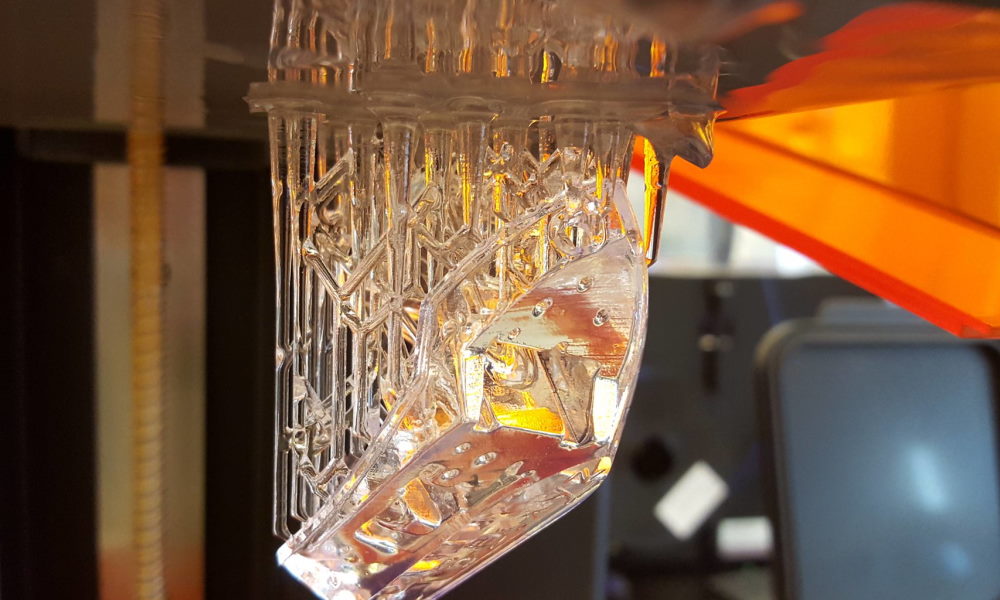

SLA, or stereolithography, is a 3D printing technique that uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid objects. The process starts by creating a 3D model in a computer-aided design (CAD) program, which is then sent to the SLA printer. The printer uses a laser to trace the cross-section of the object, curing the liquid resin and building up the object layer by layer. SLA printing is known for its high resolution and fine details, making it a popular choice for creating prototypes, jewelry, and other small objects.
Typical Material for SLA Printing
- Photopolymer Resin: This is the most common material used in SLA printing. It is a liquid that is cured by a UV laser to form solid objects. Photopolymer resin is available in a wide range of colors and types, including clear, flexible, and high-temperature resistant resins.
- Composite Resin: This type of resin contains particles such as metals, ceramics or glass. This allows for a unique properties such as electrical conductivity, high strength and durability.
Benefits & Drawbacks of SLA printing
| Benefits of SLA Printing | Drawbacks of SLA Printing |
|---|---|
| High resolution and fine details: SLA printing is known for its ability to create highly detailed and precise objects, making it a great choice for prototypes, jewelry, and other small objects. | Limited materials: SLA printing is typically limited to using liquid resin, which can be more expensive than other materials. |
| Fast printing speed: SLA printers are generally faster than FDM printers, allowing for faster turnaround times. | Limited build volume: SLA printers typically have a smaller build volume than FDM printers, which can limit the size of the objects that can be printed. |
| Smooth surface finish: SLA printed objects have a smooth surface finish, which can save time and money on post-processing. | UV-sensitive resin: The liquid resin used in SLA printing is UV sensitive, so it needs to be stored and post-processed in a UV-free environment. |
Common Applications for SLA Printing
SLA printing has a wide range of real-life applications that are widely used in different fields, from creating accurate medical models, intricate jewelry designs, functional prototypes for aerospace and automotive, and even in the entertainment industry for creating detailed props. The high resolution and fine details of SLA printing make it a versatile technology that is suitable for a wide range of projects.
Dental and Medical Models: SLA printing is widely used in the dental and medical field for creating precise and accurate models of human anatomy. Dentists and orthodontists use SLA printed models for planning and practicing complex procedures such as jaw surgery, dental implants, and orthodontic treatment. Additionally, medical researchers and educators use SLA printed models for studying human anatomy and for creating training aids for medical students.
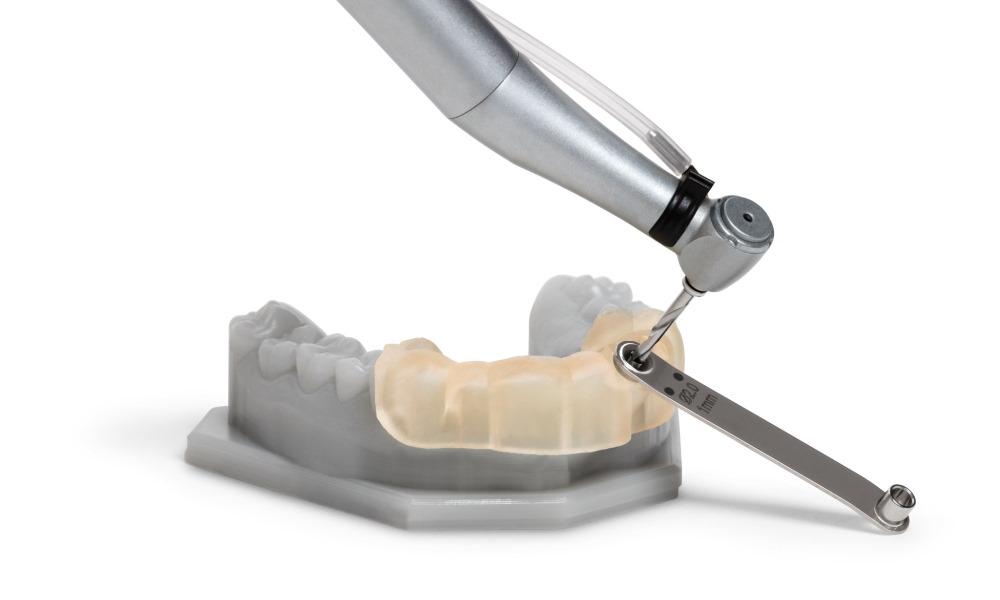
Automotive and aerospace prototypes: SLA printing is ideal for creating precise, detailed, and functional prototypes for industries like aerospace and automotive. SLA printing allows engineers and designers to quickly create accurate models of complex parts and assemblies that can be used for testing and evaluation. Additionally, SLA printing enables the creation of lightweight and durable parts that can be used in aerospace and automotive applications.
Jewelry: The high resolution and fine details of SLA printing make it a great choice for creating intricate jewelry designs. SLA printing allows jewelers to create highly detailed and precise models of their designs, which can then be used to create molds for casting. Additionally, SLA printing enables the creation of unique and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional jewelry-making methods.
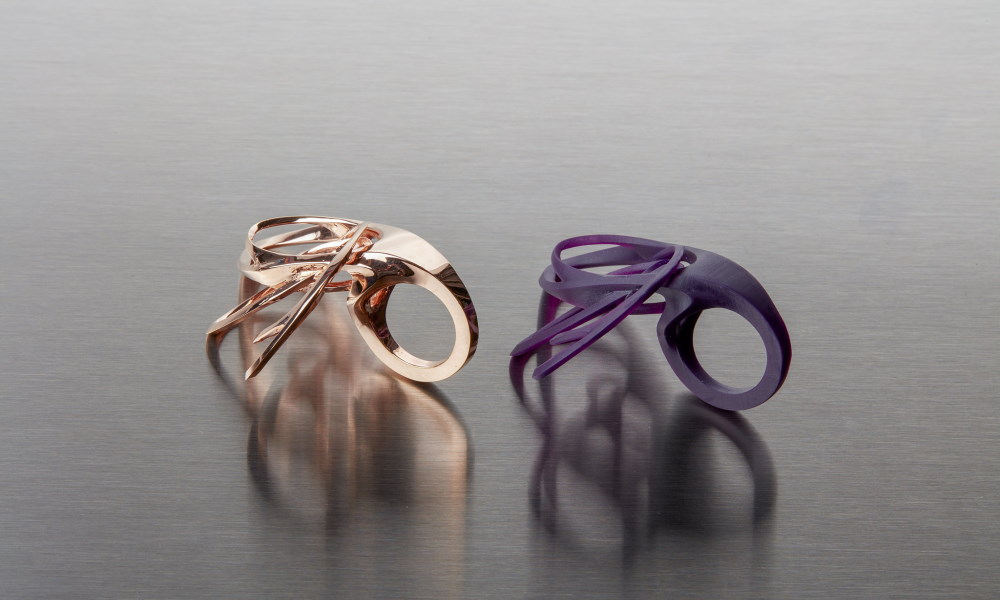

Cosplay and Prop Making: The high resolution and fine details of SLA printing make it a great choice for creating cosplay and prop. The ability to print in different colors and materials allow the creation of very detailed and realistic props that can be used in movies, TV shows, and video games.
What is FDM Printing?
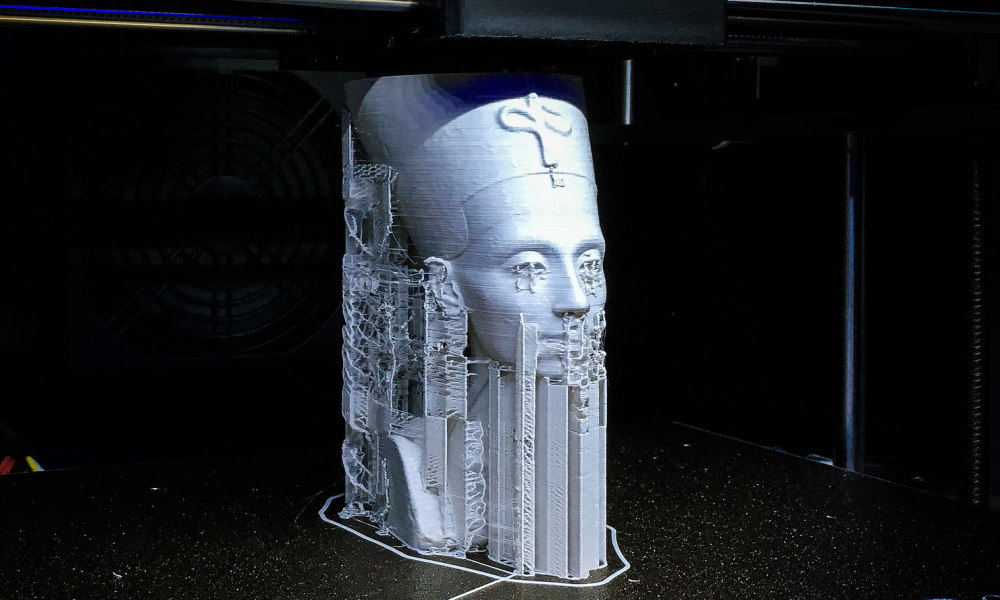
FDM, or fused deposition modeling, is a 3D printing technique that uses a thermoplastic filament that is heated and extruded through a nozzle, building up the object layer by layer. Like SLA printing, FDM printing starts with a 3D model in a CAD program, which is then sent to the FDM printer. FDM printing is known for its strength and durability, making it a popular choice for creating functional parts, toys, and other objects that need to be sturdy.
Popular Materials for FDM Printing
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): This is a strong, durable, and heat-resistant thermoplastic that is commonly used in FDM printing. It is widely used for creating functional parts and prototypes.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): This is a biodegradable thermoplastic that is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch. It is a popular choice for creating toys, figurines, and other objects.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): This is a flexible and durable thermoplastic that is commonly used in FDM printing to create flexible parts such as phone cases and other protective gear.
Benefits & Drawbacks of FDM printing
| Benefits of FDM Printing | Drawbacks of FDM Printing |
|---|---|
| Wide range of materials: FDM printing can use a wide range of thermoplastic materials, including ABS, PLA, and TPU, which can offer different properties such as flexibility, transparency, and high-temperature resistance. | Lower resolution and detail: FDM printing is not as precise as SLA printing, and the objects produced may not have as fine a level of detail. |
| Large build volume: FDM printers typically have a larger build volume than SLA printers, which allows for larger objects to be printed. | Post-processing: FDM printed objects often require additional post-processing, such as sanding or painting, to achieve a smooth surface finish. |
| Low cost: FDM printing is generally less expensive than SLA printing, as the materials used are often less expensive |
Real-life Applications for FDM Printing
FDM printing is a versatile technology that is widely used in a variety of industries and fields due to its strength and durability. From creating functional parts and prototypes to creating parts for robots and for educational purposes, FDM printing has a wide range of real-world applications that makes it suitable for a wide range of projects and industries.
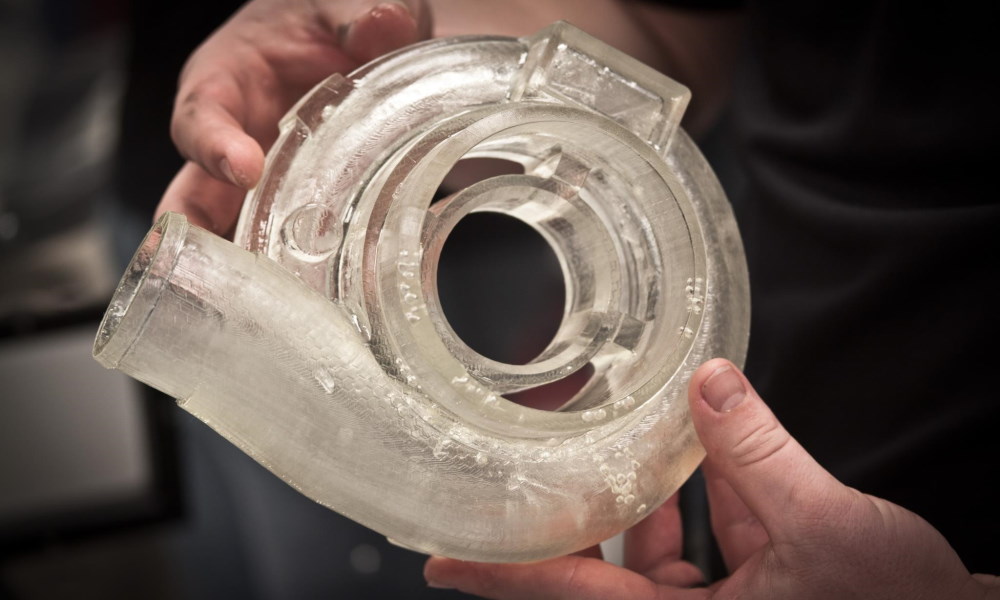
Manufacturing: FDM printing is commonly used for creating functional parts, fixtures, and jigs in the manufacturing industry. The ability to print in a wide range of materials, including ABS, PLA, and TPU, makes FDM printing suitable for a wide range of applications. From creating small parts such as gears, brackets, and other mechanical components to larger ones like end-use products, FDM printing has a wide range of applications in the manufacturing industry.

Robotics: FDM printing is useful for creating parts for robots, such as gears, brackets, and other mechanical components. The ability to print in a wide range of materials, including ABS, PLA, and TPU, makes FDM printing suitable for creating a wide range of robotic parts and components. Additionally, the strength and durability of FDM printed parts to make them suitable for use in demanding environments and applications, such as in industrial robots.
Prototyping: FDM printing is an affordable and quick way to create functional prototypes for product design. Its ability to use a wide range of materials, including ABS, PLA, and TPU, makes it ideal for creating prototypes for a wide range of products, from consumer goods to industrial equipment. The ability to print quickly and easily allows for rapid iteration and testing of designs, which can greatly speed up the product development process.

Education: FDM printing is also used in education as it allows students to learn about 3D printing and manufacturing, and to create projects using the technology. It is a great way to introduce students to the world of design and engineering.
Resin or Filament, what is the big difference?
Resin (SLA) and filament (FDM) are two different types of materials that are used in 3D printing. Resin, which is used in SLA printing, is a liquid that is cured by a UV laser to form solid objects. Filament, which is used in FDM printing, is a thermoplastic material that is extruded through a nozzle to create an object.
The way of using these materials is different as well. SLA printing requires the use of a UV laser to cure the liquid resin into a solid object, while FDM printing uses a heated nozzle to extrude the filament and build up the object layer by layer. Additionally, SLA printing generally requires a post-processing step to remove the object from the build plate and to clean off any excess resin, while FDM printing does not typically require post-processing.
Resin offers high resolution and fine details. Additionally, it comes in a wide range of colors and types, including clear, flexible, and high-temperature-resistant resins. However, compared to filament, the range of material is definitely more limited.
In summary, resin and filament are two different types of materials that are used in 3D printing, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Resin is used in SLA printing and offers high resolution and fine details, while filament is used in FDM printing and offers a wide range of materials and properties. The way of using these materials also differs, with SLA printing requiring a UV laser to cure the resin and post-processing to remove the object, while FDM printing uses a heated nozzle to extrude the filament and does not typically require post-processing.
Takeaways
In conclusion, SLA and FDM are both great 3D printing techniques, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. SLA printing is known for its high resolution and fine details, making it a great choice for creating prototypes, jewelry, and other small objects. FDM printing, on the other hand, is known for its strength and durability, making it a popular choice for creating functional parts, toys, and other objects that need to be sturdy. When choosing between SLA and FDM printing, it is important to consider the specific needs of your project and the materials and applications that best suit your project.
